يمكن تعريف المصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد على أنها مصفوفة من المصفوفات. يتم تنظيم المصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد كمصفوفات يمكن تمثيلها كمجموعة من الصفوف والأعمدة.
ومع ذلك، يتم إنشاء صفائف ثنائية الأبعاد لتنفيذ قاعدة بيانات علائقية تشبه بنية البيانات. فهو يوفر سهولة الاحتفاظ بكميات كبيرة من البيانات في وقت واحد والتي يمكن تمريرها إلى أي عدد من الوظائف حيثما كان ذلك مطلوبًا.
كيفية الإعلان عن صفيف ثنائي الأبعاد
إن بناء جملة الإعلان عن مصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد يشبه إلى حد كبير صياغة مصفوفة أحادية البعد، كما يلي.
حاول التقاط جافا
int arr[max_rows][max_columns];
ومع ذلك، فإنه ينتج بنية البيانات التي تبدو كما يلي.
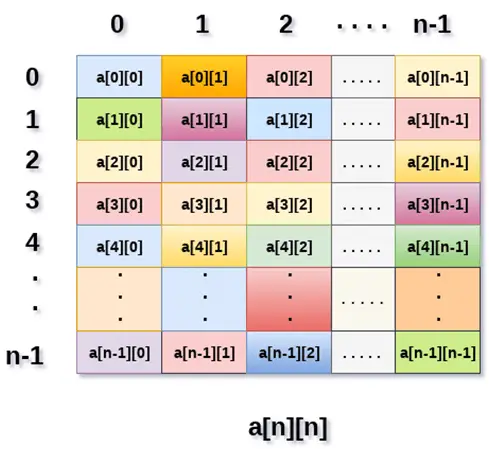
الصورة أعلاه توضح المصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد، والعناصر منظمة على شكل صفوف وأعمدة. يتم تمثيل العنصر الأول من الصف الأول بـ [0] [0] حيث الرقم الموضح في الفهرس الأول هو رقم ذلك الصف بينما الرقم الموضح في الفهرس الثاني هو رقم العمود.
كيف يمكننا الوصول إلى البيانات في مجموعة ثنائية الأبعاد
نظرًا لحقيقة أنه يمكن الوصول بشكل عشوائي إلى عناصر المصفوفات ثنائية الأبعاد. كما هو الحال مع المصفوفات ذات البعد الواحد، يمكننا الوصول إلى الخلايا الفردية في مصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد باستخدام مؤشرات الخلايا. هناك مؤشران مرتبطان بخلية معينة، أحدهما هو رقم الصف الخاص بها والآخر هو رقم العمود الخاص بها.
ومع ذلك، يمكننا تخزين القيمة المخزنة في أي خلية معينة من مصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد إلى متغير x باستخدام الصيغة التالية.
int x = a[i][j];
حيث i وj هو رقم الصف والعمود للخلية على التوالي.
ج ++ واجهة المستخدم الرسومية
يمكننا تعيين كل خلية في مصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد إلى 0 باستخدام الكود التالي:
for ( int i=0; i<n ;i++) { for (int j="0;" j<n; j++) a[i][j]="0;" } < pre> <h2>Initializing 2D Arrays </h2> <p>We know that, when we declare and initialize one dimensional array in C programming simultaneously, we don't need to specify the size of the array. However this will not work with 2D arrays. We will have to define at least the second dimension of the array. </p> <p>The syntax to declare and initialize the 2D array is given as follows. </p> <pre> int arr[2][2] = {0,1,2,3}; </pre> <p>The number of elements that can be present in a 2D array will always be equal to ( <strong>number of rows * number of columns</strong> ). </p> <p> <strong>Example :</strong> Storing User's data into a 2D array and printing it. </p> <p> <strong>C Example : </strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf('enter a[%d][%d]: ',i,j); scanf('%d',&arr[i][j]); } printf('
printing the elements ....
'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf('
'); printf('%d ',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print('enter element'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println('printing elements...'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+' '); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline('enter element'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline('printing elements...'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+' '); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></n> سيكون دائمًا عدد العناصر التي يمكن أن تكون موجودة في مصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد مساويًا لـ ( عدد الصفوف * عدد الأعمدة ).
مثال : تخزين بيانات المستخدم في مصفوفة ثنائية الأبعاد وطباعتها.
ج مثال :
#include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf(\'enter a[%d][%d]: \',i,j); scanf(\'%d\',&arr[i][j]); } printf(\'
printing the elements ....
\'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf(\'
\'); printf(\'%d \',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print(\'enter element\'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println(\'printing elements...\'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+\' \'); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline(\'enter element\'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline(\'printing elements...\'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+\' \'); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)> حيث B. A. هو العنوان الأساسي أو عنوان العنصر الأول في المصفوفة a[0][0] .
مثال :
طريقة التبديل جافا
a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer
حسب عمود النظام الرئيسي
إذا تم الإعلان عن المصفوفة بواسطة a[m] [n] حيث m هو عدد الصفوف بينما n هو عدد الأعمدة، فسيتم حساب عنوان العنصر a[i] [j] من المصفوفة المخزنة في ترتيب الصف الرئيسي كـ ,
Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA
حيث BA هو العنوان الأساسي للمصفوفة.
مثال:
A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes
