ال for حلقة في لغة C يتم استخدامه لتكرار العبارات أو جزء من البرنامج عدة مرات. يتم استخدامه بشكل متكرر لاجتياز هياكل البيانات مثل المصفوفة والقائمة المرتبطة.
بناء الجملة للحلقة في C
بناء جملة for Loop في لغة C موضح أدناه:
مقارنة السلسلة في Java
for(Expression 1; Expression 2; Expression 3){ //code to be executed } مخطط انسيابي للحلقة في C
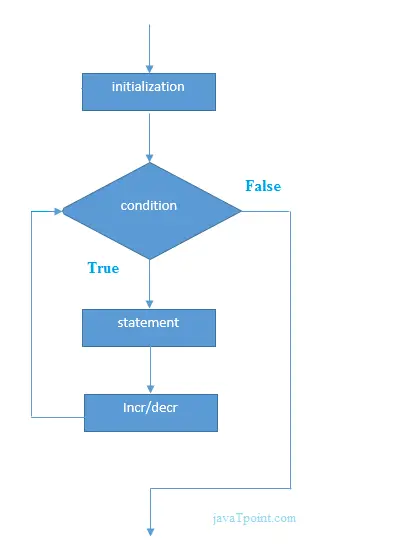
C لأمثلة الحلقة
دعونا نرى البرنامج البسيط للحلقة الذي يطبع جدول 1.
#include int main(){ int i=0; for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf('%d
',i); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 </pre> <h3>C Program: Print table for the given number using C for loop</h3> <pre> #include int main(){ int i=1,number=0; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf('%d
',(number*i)); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 1</h3> <ul> <li>The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.</li> <li>We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.</li> <li>Expression 1 is optional.</li> <li>In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf('%d ',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf('%d %d %d
',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf('%d %d
',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)></pre></=10;i++){></pre></=10;i++){> برنامج C: طباعة جدول للرقم المحدد باستخدام C للحلقة
#include int main(){ int i=1,number=0; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf(\'%d
\',(number*i)); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 1</h3> <ul> <li>The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.</li> <li>We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.</li> <li>Expression 1 is optional.</li> <li>In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf(\'%d \',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)></pre></=10;i++){> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
خصائص التعبير 1
- يمثل التعبير تهيئة متغير الحلقة.
- يمكننا تهيئة أكثر من متغير في Expression 1.
- التعبير 1 اختياري.
- في لغة C، لا يمكننا الإعلان عن المتغيرات في Expression 1. ومع ذلك، يمكن أن يكون ذلك استثناءً في بعض المترجمين.
مثال 1
#include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf(\'%d \',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)> مثال 2
#include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)> خصائص التعبير 2
- التعبير 2 هو تعبير شرطي. إنه يتحقق من استيفاء شرط معين. إذا لم يكن الأمر كذلك، فسيتم إنهاء الحلقة.
- يمكن أن يحتوي التعبير 2 على أكثر من شرط واحد. ومع ذلك، سوف تتكرر الحلقة حتى يصبح الشرط الأخير خاطئًا. سيتم التعامل مع الشروط الأخرى كبيانات.
- التعبير 2 اختياري.
- يمكن أن يؤدي التعبير 2 مهمة التعبير 1 والتعبير 3. أي أنه يمكننا تهيئة المتغير بالإضافة إلى تحديث متغير الحلقة في التعبير 2 نفسه.
- يمكننا تمرير قيمة صفر أو قيمة غير صفرية في التعبير 2. ومع ذلك، في لغة C، أي قيمة غير الصفر تكون صحيحة، والصفر خطأ افتراضيًا.
مثال 1
#include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)> مثال 2
#include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\\'%d %d %d
\\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\\'%d %d
\\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)> مثال 3
حجم المتجه c++
#include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } انتاج |
ب+ الأشجار
infinite loop
خصائص التعبير 3 - يتم استخدام التعبير 3 لتحديث متغير الحلقة.
- يمكننا تحديث أكثر من متغير في نفس الوقت.
- التعبير 3 اختياري.
مثال 1
#include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\\'%d %d
\\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)> هيئة الحلقة
يتم استخدام الأقواس {} لتحديد نطاق الحلقة. ومع ذلك، إذا كانت الحلقة تحتوي على عبارة واحدة فقط، فلن نحتاج إلى استخدام الأقواس. من الممكن حدوث حلقة بدون جسم. تعمل الأقواس كفاصل كتلة، أي أن متغير القيمة المعلن داخل حلقة for صالح فقط لتلك الكتلة وليس خارجها. النظر في المثال التالي.
#include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)> صيغة المصدر للحلقة في C
لجعل حلقة for لا نهائية، لا نحتاج إلى إعطاء أي تعبير في بناء الجملة. بدلاً من ذلك، نحن بحاجة إلى توفير فاصلتين منقوطة للتحقق من صحة بناء جملة الحلقة. سيعمل هذا كحلقة لا نهائية.
#include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } إذا قمت بتشغيل هذا البرنامج، سوف ترى البيان أعلاه مرات لا حصر لها.
