شجرة ثنائية عبارة عن بنية بيانات غير خطية من النوع الشجري تُستخدم بشكل أساسي للفرز والبحث لأنها تخزن البيانات في شكل هرمي. في هذا القسم سوف نتعلم تنفيذ بنية بيانات الشجرة الثنائية في Java . كما يوفر وصفًا موجزًا لبنية بيانات الشجرة الثنائية.
شجرة ثنائية
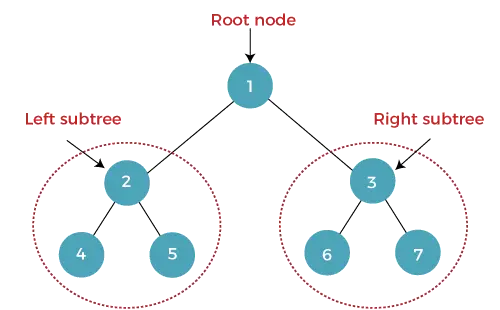
تسمى الشجرة التي تحتوي كل عقدة (أصلية) فيها على الأكثر على عقدتين تابعتين (يسارًا ويمينًا) بالشجرة الثنائية. تسمى العقدة العلوية بالعقدة الجذرية. في الشجرة الثنائية، تحتوي العقدة على البيانات والمؤشر (العنوان) للعقدة الفرعية اليمنى واليسرى.
ال ارتفاع من شجرة ثنائية هو عدد الحواف بين جذر الشجرة وأبعد (أعمق) ورقة لها. إذا كانت الشجرة فارغ ، الارتفاع هو 0 . يتم الإشارة إلى ارتفاع العقدة بواسطة ح .
ارتفاع الشجرة الثنائية أعلاه هو 2.
كيف يمكنني العثور على التطبيقات المخفية على أندرويد
يمكننا حساب عدد الأوراق والعقدة باستخدام الصيغة التالية.
- الحد الأقصى لعدد العقد الورقية عبارة عن شجرة ثنائية: 2ح
- الحد الأقصى لعدد العقد عبارة عن شجرة ثنائية: 2ح+1-1
حيث h هو ارتفاع الشجرة الثنائية.
مثال على الشجرة الثنائية

أنواع الشجرة الثنائية
هناك الأنواع التالية من الشجرة الثنائية في بنية البيانات:
- شجرة ثنائية كاملة/بدقة
- شجرة ثنائية كاملة
- شجرة ثنائية مثالية
- توازن الشجرة الثنائية
- شجرة ثنائية الجذور
- شجرة ثنائية متدهورة/مرضية
- شجرة ثنائية موسعة
- شجرة ثنائية منحرفة
- شجرة ثنائية منحرفة إلى اليسار
- شجرة ثنائية منحرفة إلى اليمين
- شجرة ثنائية مترابطة
- شجرة ثنائية مترابطة واحدة
- شجرة ثنائية الخيوط مزدوجة
تنفيذ الشجرة الثنائية في جافا
هناك طرق عديدة لتنفيذ الشجرة الثنائية. في هذا القسم، سنقوم بتنفيذ الشجرة الثنائية باستخدام بنية بيانات LinkedList. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، سنقوم أيضًا بتنفيذ أوامر الاجتياز والبحث عن عقدة وإدراج عقدة في شجرة ثنائية.
تنفيذ الشجرة الثنائية باستخدام LinkedList
خوارزمية
تحديد فئة العقدة التي تحتوي على ثلاث سمات وهي: البيانات اليسرى واليمنى. هنا يمثل اليسار الابن الأيسر للعقدة ويمثل اليمين الابن الأيمن للعقدة.
- عند إنشاء عقدة، سيتم تمرير البيانات إلى سمة البيانات الخاصة بالعقدة وسيتم تعيين كل من اليسار واليمين على قيمة خالية.
- حدد فئة أخرى لها جذر السمة.
- يمثل الجذر العقدة الجذرية للشجرة ويقوم بتهيئتها لتصبح خالية.
- يتحقق مما إذا كان الجذر فارغًا، مما يعني أن الشجرة فارغة. سيتم إضافة العقدة الجديدة كجذر.
- وإلا فإنه سيتم إضافة الجذر إلى قائمة الانتظار.
- تمثل العقدة المتغيرة العقدة الحالية.
- أولاً، يتحقق ما إذا كانت العقدة تحتوي على فرع يسار ويمين. إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، فسيتم إضافة كلا العقدتين إلى قائمة الانتظار.
- إذا لم يكن الطفل الأيسر موجودًا، فسيتم إضافة العقدة الجديدة باعتبارها الطفل الأيسر.
- إذا كان اليسار موجودًا، فسيتم إضافة العقدة الجديدة باعتبارها العقدة اليمنى.
- إنه يجتاز الشجرة بأكملها ثم يطبع الطفل الأيسر متبوعًا بالجذر ثم يتبعه الطفل الأيمن.
BinarySearchTree.java
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } انتاج:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
عمليات الشجرة الثنائية
يمكن تنفيذ العمليات التالية على شجرة ثنائية:
- إدراج
- حذف
- يبحث
- اجتياز
برنامج جافا لإدراج عقدة في شجرة ثنائية
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } انتاج:
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
برنامج جافا لحذف عقدة في جافا
خوارزمية
- بدءًا من الجذر، ابحث عن العقدة الأعمق والأكثر يمينًا في الشجرة الثنائية والعقدة التي نريد حذفها.
- استبدل بيانات العقدة الأعمق في أقصى اليمين بالعقدة المراد حذفها.
- ثم احذف أعمق عقدة في أقصى اليمين.
النظر في الشكل التالي.

حذفNode.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } انتاج:
علامات HTML
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
برنامج جافا للبحث عن عقدة في شجرة ثنائية
خوارزمية
- تحديد فئة العقدة التي لها ثلاث سمات وهي: البيانات اليسرى واليمنى. هنا يمثل اليسار الابن الأيسر للعقدة ويمثل اليمين الابن الأيمن للعقدة.
- عند إنشاء عقدة، سيتم تمرير البيانات إلى سمة البيانات الخاصة بالعقدة وسيتم تعيين كل من اليسار واليمين على قيمة فارغة.
- حدد فئة أخرى تحتوي على جذر السمة والعلم.
- يمثل الجذر العقدة الجذرية للشجرة ويقوم بتهيئتها لتصبح فارغة.
- سيتم استخدام العلامة للتحقق مما إذا كانت العقدة المحددة موجودة في الشجرة أم لا. في البداية، سيتم ضبطه على خطأ.
- يتحقق مما إذا كان الجذر فارغًا، مما يعني أن الشجرة فارغة.
- إذا لم تكن الشجرة فارغة، فسوف تقارن بيانات درجة الحرارة بالقيمة. إذا كانوا متساوين، فإنه سيتم تعيين العلم إلى صحيح والعودة.
- اجتياز الشجرة الفرعية اليسرى عن طريق استدعاء searchNode() بشكل متكرر والتحقق مما إذا كانت القيمة موجودة في الشجرة الفرعية اليسرى.
- اجتياز الشجرة الفرعية اليمنى عن طريق استدعاء searchNode() بشكل متكرر والتحقق مما إذا كانت القيمة موجودة في الشجرة الفرعية اليمنى.
SearchBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } انتاج:
Element is present in the binary tree.
اجتياز الشجرة الثنائية
| ترتيب العبور | الزيارة الأولى | الزيارة الثانية | الزيارة الثالثة |
|---|---|---|---|
| مرتب | قم بزيارة الشجرة الفرعية اليسرى بالترتيب | قم بزيارة العقدة الجذرية | قم بزيارة الشجرة الفرعية الصحيحة بالترتيب |
| النظام السابق | قم بزيارة العقدة الجذرية | قم بزيارة الشجرة الفرعية اليسرى في الطلب المسبق | قم بزيارة الشجرة الفرعية الصحيحة في الطلب المسبق |
| طلب بريدي | قم بزيارة الشجرة الفرعية اليسرى في الطلب اللاحق | قم بزيارة الشجرة الفرعية الصحيحة في الطلب اللاحق | قم بزيارة العقدة الجذرية |
ملحوظة: باستثناء عمليات الاجتياز الثلاثة المذكورة أعلاه، هناك ترتيب اجتياز آخر يسمى اجتياز الحدود.
برنامج Java لاجتياز الطلب الداخلي والطلب المسبق واجتياز الطلب اللاحق
BinaryTree.java
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } انتاج:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
إلى جانب العمليات المذكورة أعلاه، يمكننا أيضًا إجراء عمليات مثل العقدة الكبيرة وأصغر العقدة ومجموع جميع العقد.
برنامج جافا للعثور على أكبر عقدة في الشجرة الثنائية
أكبر عقدة.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } انتاج:
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
برنامج جافا للعثور على أصغر عقدة في الشجرة الثنائية
خوارزمية
- تحديد فئة العقدة التي لها ثلاث سمات وهي: البيانات، اليسار واليمين. هنا يمثل اليسار الابن الأيسر للعقدة ويمثل اليمين الابن الأيمن للعقدة.
- عند إنشاء عقدة، سيتم تمرير البيانات إلى سمة بيانات العقدة وسيتم تعيين كل من اليسار واليمين على قيمة فارغة.
- حدد فئة أخرى لها جذر السمة.
جذر تمثل العقدة الجذرية للشجرة وتهيئتها لتصبح خالية.
- فإنه يتحقق ما إذا كان الجذر فارغ مما يعني أن الشجرة فارغة.
- إذا لم تكن الشجرة فارغة، فحدد المتغير min الذي سيقوم بتخزين بيانات درجة الحرارة.
- اكتشف الحد الأدنى للعقدة في الشجرة الفرعية اليسرى عن طريق استدعاء أصغر عنصر () بشكل متكرر. قم بتخزين هذه القيمة في leftMin. قارن قيمة min مع leftMin وقم بتخزين ما لا يقل عن اثنين إلى min.
- اكتشف الحد الأدنى للعقدة في الشجرة الفرعية اليمنى عن طريق استدعاء أصغر عنصر () بشكل متكرر. قم بتخزين هذه القيمة في rightMin. قارن قيمة min مع rightMin وقم بتخزين الحد الأقصى من اثنين إلى min.
- في النهاية، min سوف يحمل أصغر عقدة في الشجرة الثنائية.
SmallestNode.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } انتاج:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
برنامج جافا للعثور على الحد الأقصى لعرض شجرة ثنائية
خوارزمية
- تحديد فئة العقدة التي لها ثلاث سمات وهي: البيانات اليسرى واليمنى. هنا يمثل اليسار الابن الأيسر للعقدة ويمثل اليمين الابن الأيمن للعقدة.
- عند إنشاء عقدة، سيتم تمرير البيانات إلى سمة البيانات الخاصة بالعقدة وسيتم تعيين كل من اليسار واليمين على قيمة فارغة.
- حدد فئة أخرى لها جذر السمة.
جذر يمثل العقدة الجذرية للشجرة ويقوم بتهيئتها لتصبح فارغة.
- سيقوم maxWidth المتغير بتخزين الحد الأقصى لعدد العقد الموجودة في أي مستوى.
- يتم استخدام قائمة الانتظار لاجتياز مستوى الشجرة الثنائية.
- يتحقق مما إذا كان الجذر فارغًا، مما يعني أن الشجرة فارغة.
- إذا لم يكن الأمر كذلك، أضف العقدة الجذرية إلى قائمة الانتظار. العقد المتغيرة يتتبع InLevel عدد العقد في كل مستوى.
- إذا كانت قيمة العقدةNodesInLevel> 0، فقم بإزالة العقدة من مقدمة قائمة الانتظار وأضف العقدة الفرعية اليمنى واليسرى إلى قائمة الانتظار. بالنسبة للتكرار الأول، ستتم إزالة العقدة 1 وستتم إضافة العقدتين الفرعيتين 2 و3 إلى قائمة الانتظار. في التكرار الثاني، ستتم إزالة العقدة 2، وستتم إضافة العقدة الفرعية 4 و5 إلى قائمة الانتظار، وهكذا.
- سيقوم MaxWidth بتخزين الحد الأقصى (maxWidth،NodesInLevel). لذلك، في أي وقت معين، فإنه سيمثل الحد الأقصى لعدد العقد.
- سيستمر هذا حتى يتم اجتياز جميع مستويات الشجرة.
BinaryTree.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } انتاج:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
