في جافا، باطل هو حرفي. يتم استخدامه بشكل أساسي لتعيين قيمة فارغة لمتغير. من الممكن استخدام قيمة فارغة لسلسلة أو كائن أو التاريخ والوقت، وما إلى ذلك. لا يمكننا تعيين قيمة فارغة لأنواع البيانات الأولية مثل int، وfloat، وما إلى ذلك.
في البرمجة، نحتاج عادةً إلى التحقق مما إذا كان الكائن أو السلسلة فارغة أم لا لتنفيذ بعض المهام عليها. من أجل التحقق من سلسلة فارغة، لدينا بعض الطرق المحددة مسبقًا للسلسلة. لنأخذ بعض الأمثلة لأنواع البيانات المختلفة لفهم كيف يمكننا التحقق مما إذا كانت فارغة أم لا.
خيط
في Java، يمكن أن تكون السلسلة فارغة أو فارغة، وكل واحدة منها مميزة.
أمثلة على أتمتة dfa
1. السلسلة الفارغة هي كائن سلسلة له بعض القيمة، ولكن طوله يساوي الصفر. على سبيل المثال:
String str1 = ''
2. السلسلة الفارغة هي سلسلة تحتوي على مسافة بيضاء كقيمة لها. طوله دائمًا أكبر من 0 وليس فارغًا ولا فارغًا. على سبيل المثال:
String str2 = ''
3. السلسلة الفارغة ليس لها قيمة وتجعل السلسلة فارغة عن طريق تعيين أ باطل الكلمة الرئيسية كقيمة لها. على سبيل المثال:
String str3 = null
من أجل التحقق مما إذا كانت السلسلة فارغة أم لا، نستخدم عامل المقارنة (==). لنأخذ مثالاً عليه لفهم كيف يمكننا استخدامه للتحقق من القيمة الخالية.
NullCheckExample1.java
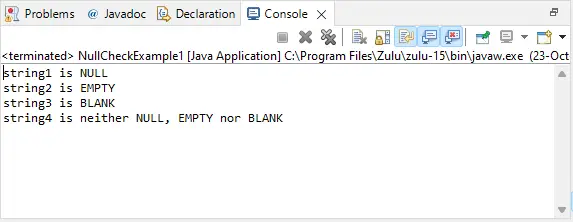
// import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; // create class NullCheckExample1 class to check whether a string is empty or null class NullCheckExample1 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args) { // create null, empty, and blank strings String string1 = null; String string2 = ''; String string3 = ' '; String string4 = 'Test'; // check whether string1 is null, empty, or blank System.out.println('string1 is ' + checkNullEmptyBlank(string1)); // check whether string2 is null, empty, or blank System.out.println('string2 is ' + checkNullEmptyBlank(string2)); // check whether string3 is null, empty, or blank System.out.println('string3 is ' + checkNullEmptyBlank(string3)); // check whether string4 is null, empty, or blank System.out.println('string4 is ' + checkNullEmptyBlank(string4)); } // create checkNullEmptyBlank() method which check whether the string is empty, null or blank and return result to the main() method public static String checkNullEmptyBlank(String strToCheck) { // check whether the given string is null or not if (strToCheck == null) { return 'NULL'; } // check whether the given string is empty or not else if(strToCheck.isEmpty()) { return 'EMPTY'; } // check whether the given string is blank or not else if(strToCheck.isBlank()) { return 'BLANK'; } else { return 'neither NULL, EMPTY nor BLANK'; } } } انتاج:
كائن التاريخ والوقت
يعد كل من Date وDateTime من أنواع البيانات غير الأولية، لذا يمكنهم تخزين قيمة فارغة. لنأخذ مثالاً على كائن التاريخ والوقت لفهم كيف يمكننا التحقق من كائن تاريخ أو وقت فارغ.
أنواع الشجرة الثنائية
NullCheckExample2.java
//import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.text.ParseException; importjava.text.SimpleDateFormat; importjava.util.Date; importjava.util.Scanner; //create class NullCheckExample2 class to check whether the Date object is null or not public class NullCheckExample2 { // declare a variable of date type and initialize it with null public static Date d1 = null; public static Date finalResult; // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // declare a variable of type string that will store the user-entered date in string format String d2; // create scanner class object Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Date in dd/mm/yyyy format:'); // take input from user and initialize variable d2 = sc.nextLine(); // close scanner class obj sc.close(); // create an instance of the SimpleDateFormat class for modifying the date object SimpleDateFormatobj = new SimpleDateFormat('dd/MM/yyyy'); // use try-catch to parse string to date try { finalResult = obj.parse(d2); } catch (ParseException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // check whether date1 and date2 is null or not by using comparison operator if(d1 == null) { System.out.println('Date d1 is NULL.'); } if(finalResult == null) { System.out.println('Date d2 is NULL.'); }else { System.out.println('Date d2 is not NULL.'); } } } انتاج:

كائن جافا
من أجل التحقق مما إذا كان كائن Java خاليًا أم لا، يمكننا إما استخدام طريقة isNull() لـ أشياء عامل الطبقة أو المقارنة. لنأخذ مثالاً لفهم كيف يمكننا استخدام طريقة isNull() أو عامل المقارنة للتحقق من قيمة كائن Java.
NullCheckExample3.java
// import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; // create NullCheckExample3 class to check whether Java object is null or not public class NullCheckExample3 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args) { // create instance of User2 User2 userObj = new User2(); // get data of User2 by calling User1 firstUser = userObj.getFirstUser(); // check whether firstUser is null or not if (firstUser == null) { System.out.println('Object is Null'); } else { System.out.println('Object is not Null'); // set name for user1 firstUser.setName('Paul'); System.out.println(firstUser.getName()); } } } // create User1 class having a name attribute class User1 { // declare name variable String name; // getter for getting name of User1 public String getName() { // return name of User1 return name; } // setter for setting name of User1 public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } // create class User2 having variable of type User1 class User2 { User1 obj; // getter to get object of User1 public User1 getFirstUser() { returnobj; } } انتاج:
جافا بارسينت

NullCheckExample4.java
// import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.util.Objects; // create NullCheckExample3 class to check whether Java object is null or not public class NullCheckExample4 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args) { // create instance of User2 User2 userObj = new User2(); // get data of User2 by calling User1 firstUser = userObj.getFirstUser(); // check whether firstUser is null or not if (Objects.isNull(firstUser) ){ System.out.println('Object is Null'); } else { System.out.println('Object is not Null'); // set name for user1 firstUser.setName('Paul'); System.out.println(firstUser.getName()); } } } // create User1 class having a name attribute class User1 { // declare name variable String name; // getter for getting name of User1 public String getName() { // return name of User1 return name; } // setter for setting name of User1 public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } // create class User2 having variable of type User1 class User2 { User1 obj; // getter to get object of User1 public User1 getFirstUser() { returnobj; } } انتاج:

