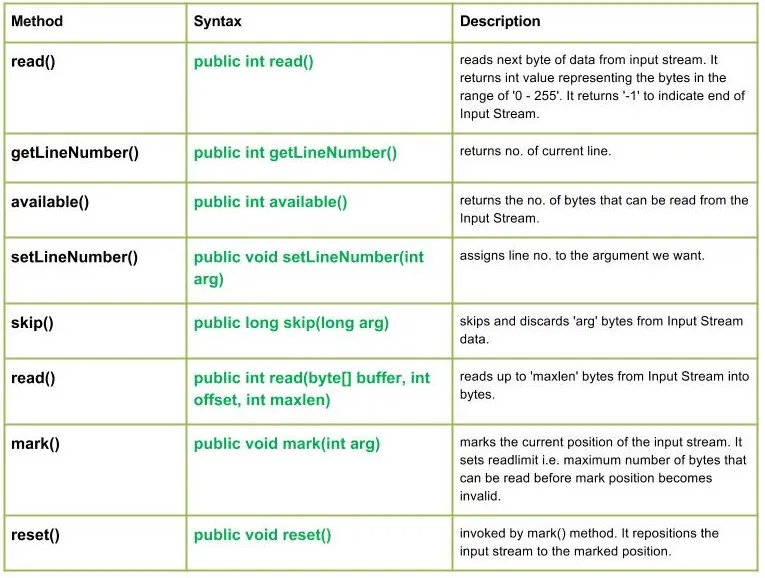
فئة java.io.LineNumberInputStream هي ببساطة امتداد لتدفق الإدخال مما يوفر وسيلة إضافية للاحتفاظ بسجل رقم السطر الحالي.
خط عبارة عن سلسلة من البايتات تنتهي بـ : 'r'، أي حرف إرجاع أو حرف السطر الجديد: 'n' أو حرف تغذية يتبع حرف الإرجاع.
تصريح :
public class LineNumberInputStream extends Reader
البنائين :
LineNumberInputStream(InputStream in) : Constructs a newline no. stream that reads it's input from the specified Input Stream.
طُرق:
مجاني مقابل مجاني
بناء الجملة :
public int read() Parameters : ------- Return : int value representing the bytes in the range of '0 - 255'. return -1 indicating end of Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
تطبيق :
Java// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; System.out.print(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
ملحوظة :
لن يتم تشغيل كود Java التالي هنا حيث لا يمكننا الوصول إلى أي ملف على IDE عبر الإنترنت.
لذا انسخ البرنامج إلى نظامك وقم بتشغيله هناك.
ال ABC.txt الملف المستخدم في البرنامج يحتوي على :
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
الإخراج :
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
بناء الجملة :
public int getLineNumber() Parameters : ------- Return : no. of current line
تطبيق :
Java// Java program illustrating the working of getLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try { char c; int a b; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of getLineNumber() : to print line no. a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(' At line : ' + a); System.out.print(c); } a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(' at line: ' + a); } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
ملحوظة :
لن يتم تشغيل كود Java التالي هنا حيث لا يمكننا الوصول إلى أي ملف على IDE عبر الإنترنت.
لذا انسخ البرنامج إلى نظامك وقم بتشغيله هناك.
ال ABC.txt الملف المستخدم في البرنامج يحتوي على :
no. of lines
الإخراج :
At line : 0 n At line : 0 o At line : 0 . At line : 0 At line : 0 o At line : 0 f At line : 1 At line : 1 l At line : 1 i At line : 1 n At line : 1 e At line : 1 s at line: 1
بناء الجملة :
public int available() Parameters : ------- Return : returns the no. of bytes that can be read from the Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
تطبيق :
Java// Java program illustrating the working of available() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of available method : return no. of bytes that can be read a = geekline.available(); System.out.println(c + ' Bytes available : ' + a); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
ملحوظة :
لن يتم تشغيل كود Java التالي هنا حيث لا يمكننا الوصول إلى أي ملف على IDE عبر الإنترنت.
لذا انسخ البرنامج إلى نظامك وقم بتشغيله هناك.
ال ABC.txt الملف المستخدم في البرنامج يحتوي على :
available
الإخراج :
a Bytes available : 4 v Bytes available : 3 a Bytes available : 3 i Bytes available : 2 l Bytes available : 2 a Bytes available : 1 b Bytes available : 1 l Bytes available : 0 e Bytes available : 0
بناء الجملة :
public void setLineNumber(int arg) Parameters : arg : line number to assign Return : void Exception: -----
تطبيق :
Java// Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b = 0; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of setLineNumber() : to set the line no. geekline.setLineNumber(100 + b); // getLineNumber() : returning the current line no. a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(c + ' Line No. Set : ' + a); b++; } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
ملحوظة :
لن يتم تشغيل كود Java التالي هنا حيث لا يمكننا الوصول إلى أي ملف على IDE عبر الإنترنت.
لذا انسخ البرنامج إلى نظامك وقم بتشغيله هناك.
ال ABC.txt الملف المستخدم في البرنامج يحتوي على :
LineNumber
الإخراج :
L Line No. Set : 100 i Line No. Set : 101 n Line No. Set : 102 e Line No. Set : 103 N Line No. Set : 104 u Line No. Set : 105 m Line No. Set : 106 b Line No. Set : 107 e Line No. Set : 108 r Line No. Set : 109
بناء الجملة :
public long skip(long arg) Parameters : arg : no. of bytes of Input Stream data to skip. Return : no. of bytes to be skipped Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
تطبيق :
Java// Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b = 0; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // skip() : to skip and discard 'arg' bytes // Here skip() will skip and discard 3 bytes. geekline.skip(3); System.out.println(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally{ // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
ملحوظة :
لن يتم تشغيل كود Java التالي هنا حيث لا يمكننا الوصول إلى أي ملف على IDE عبر الإنترنت.
لذا انسخ البرنامج إلى نظامك وقم بتشغيله هناك.
ال ABC.txt الملف المستخدم في البرنامج يحتوي على :
Program Explaining Skip() method
الإخراج : '
P r E a n k ) t
بناء الجملة :
public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : buffer whose data to read offset : starting offset of the data maxlen : max. no. of bytes to read Return : total no. of bytes else return -1 if End of Input Stream is identified Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
تطبيق :
Java// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while((a=geekline.read())!=-1) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; System.out.print(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
ملحوظة :
لن يتم تشغيل كود Java التالي هنا حيث لا يمكننا الوصول إلى أي ملف على IDE عبر الإنترنت.
لذا انسخ البرنامج إلى نظامك وقم بتشغيله هناك.
ال ABC.txt الملف المستخدم في البرنامج يحتوي على :
Read() method
ما تفعله الطريقة هو الإزاحة = r و maxlen = 5... لذا --- أي 3 إزاحة ثم 5 بايت، أي قراءة (ثم إزاحة مرة أخرى -
الإخراج :
The number of char read: 5 ---Read(--
بناء الجملة :
public void mark(int arg) Parameters : arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream Return : void
بناء الجملة :
public void reset() Parameters : ---- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
برنامج جافا يشرح أساليب فئة LineNumberInputStream: إعادة تعيين () وعلامة ()
Java// Java program illustrating the working of LineNumberInputStream method // mark() and reset() import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geek = null; try{ geek = new FileInputStream('GEEKS.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geek); // read() method : reading and printing Characters one by one System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); // mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream geekline.mark(0); // skip() : it results in reading of 'e' in G'e'eeks geekline.skip(1); System.out.println('skip() method comes to play'); System.out.println('mark() method comes to play'); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); boolean check = geekline.markSupported(); if(geekline.markSupported()) { // reset() method : repositioning the stream to marked positions. geekline.reset(); System.out.println('reset() invoked'); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); } else { System.out.println('reset() method not supported.'); } System.out.println('geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : ' + check); } catch(Exception except) { // in case of I/O error except.printStackTrace(); } finally { // releasing the resources back to the GarbageCollector when closes if(geek != null) geek.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
ملحوظة :
لن يتم تشغيل هذا الرمز على IDE عبر الإنترنت حيث لا يوجد مثل هذا الملف هنا.
يمكنك تشغيل هذا الرمز على نظامك للتحقق من العمل.
ABC.txt الملف المستخدم في التعليمات البرمجية لديه
HelloGeeks
الإخراج :
Char : H Char : e Char : l skip() method comes to play mark() method comes to play Char : o Char : G Char : e reset() method not supported. geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : false