إعطاء ورقة مستطيلة الأبعاد أ × ب . وتتمثل المهمة في قطع الورقة بأكملها إلى الحد الأدنى عدد مربع قِطَع. يمكننا اختيار قطع مربعة من أي حجم ولكن يجب قطعها دون تداخل أو ترك أي مساحة إضافية .
أمثلة:
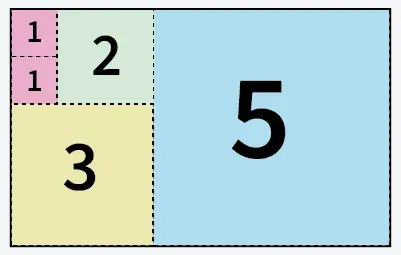
مدخل: أ = 5 ب = 8
5 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 5×8
الإخراج: 5
توضيح: يمكننا قطع الورق إلى 5 مربعات: 1 مربع بحجم 5x5 1 مربع بحجم 3x3 1 مربع بحجم 2x2 ومربعين بحجم 1x1.مدخل: أ = 13 ب = 11
6 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 13×11
الإخراج: 6
توضيح: يمكننا قطع الورق إلى 6 مربعات: 1 مربع مقاس 7x7 1 مربع مقاس 6x6 1 مربع مقاس 5x5 2 مربع مقاس 4x4 و 1 مربع مقاس 1x1.مدخل: أ = 6 ب = 7
5 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 6×7
الإخراج: 5
توضيح: يمكننا قطع الورق إلى 5 مربعات: 1 مربع بحجم 4x4، ومربعان بحجم 3x3 ومربعان بحجم 3x3.
جدول المحتويات
CSS النص الغامق
- [نهج غير صحيح 1] استخدام تقنية الجشع
- [المنهج غير الصحيح 2] استخدام البرمجة الديناميكية
- [النهج الصحيح] استخدام DFS والبرمجة الديناميكية
[نهج غير صحيح 1] استخدام تقنية الجشع
للوهلة الأولى قد يبدو أن المشكلة يمكن حلها بسهولة عن طريق قطع أكبر مربع ممكن من الورقة أولاً ثم قطع أكبر مربع من الورقة المتبقية وهكذا حتى نقطع الورقة بأكملها. لكن هذا الحل غير صحيح.
لماذا لن ينجح النهج الجشع؟
خذ بعين الاعتبار حجم الورق 6x7 فإذا حاولنا قطع الورقة بشراهة فسنحصل عليها 7 المربعات: 1 مربع الحجم 6x6 و6 مربعات الحجم 1x1 بينما الحل الصحيح هو: 5. وبالتالي فإن النهج الجشع لن ينجح.
[المنهج غير الصحيح 2] استخدام البرمجة الديناميكية
البرمجة الديناميكية مع القطع الرأسية أو الأفقية: الحل الآخر الذي قد يبدو صحيحًا هو الاستخدام البرمجة الديناميكية . يمكننا الحفاظ على جدول dp[][] بهذه الطريقة موانئ دبي [أنا] [ي] = الحد الأدنى لعدد المربعات التي يمكن قصها من ورق بهذا الحجم ط س ي . ثم لحجم الورق com.axb
اختبار البرمجيات وأنواعها
- يمكننا محاولة قصه على طول كل صف: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) حيث يمكن أن يكون k في النطاق [1 i - 1].
- يمكننا محاولة قصه على طول كل عمود: موانئ دبي [أنا] [ي] = دقيقة (dp[i] [j] 1 + dp [i] [j - k] + dp [i] [k]) حيث يمكن أن يكون k في النطاق [1 j - 1].
وأخيرا الحد الأدنى من جميع التخفيضات سيكون الجواب. ولكن هذا الحل غير صحيح أيضا.
لماذا لن ينجح القطع عموديًا أو أفقيًا باستخدام أسلوب البرمجة الديناميكية؟
لن ينجح هذا لأننا نفترض أن القطع الرأسي أو الأفقي سيقسم المستطيل دائمًا إلى قسمين. خذ بعين الاعتبار حجم الورق 13x11 ثم إذا حاولنا قطع الورقة باستخدام طريقة DP فسنحصل على 8 مربعات ولكن الإجابة الصحيحة (كما هو موضح في الأمثلة) هي 6. وبالتالي لن تعمل البرمجة الديناميكية.
[النهج الصحيح] استخدام DFS والبرمجة الديناميكية
C++ال فكرة هو قطع الورق بأكمله باستخدام DFS في تصاعدي طريقة. في كل خطوة، ابحث عن الزاوية السفلية اليسرى من الورقة وحاول قطع مربعات بجميع الأحجام الممكنة من تلك الزاوية. بعد قطع مربع، ابحث مرة أخرى عن الزاوية السفلية اليسرى من الورقة المتبقية لقص المربعات بجميع الأحجام الممكنة وهكذا. ولكن إذا جربنا جميع عمليات القطع الممكنة من الزاوية السفلية اليسرى لكل حجم ممكن من أحجام الورق، فسيكون ذلك غير فعال على الإطلاق. يمكننا تحسينه باستخدام البرمجة الديناميكية لتخزين الحد الأدنى من القطع لكل حجم ورق ممكن.
لتحديد أي حجم ورق بشكل فريد، يمكننا الحفاظ على مصفوفة remSq[] بحيث يقوم remSq[i] بتخزين عدد المربعات المتبقية ذات الحجم 1x1 في العمود رقم ith من الورقة. لذلك بالنسبة للورقة بحجم 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. أيضًا للعثور على الزاوية السفلية اليسرى، سنجد أن الفهرس الأول يحتوي على الحد الأقصى للمربعات المتبقية. حتى نتمكن من تجزئة قيمة مصفوفة remSq[] للعثور على مفتاح فريد لجميع القيم المحتملة لمصفوفة remSq[].
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
الإخراج
6
تعقيد الوقت: O(a^b) لكل عمود من الأعمدة b يمكن أن يكون لدينا مربعات.
المساحة المساعدة: O(a^b) بسبب الحفظ الذي يخزن كل حالة فريدة.

 5 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 5×8
5 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 5×8 6 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 13×11
6 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 13×11 5 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 6×7
5 مربعات مقطعة من ورق مقاس 6×7