ال حجم() يتم استخدام عامل التشغيل بشكل شائع في لغة C. وهو يحدد حجم التعبير أو نوع البيانات المحدد في عدد وحدات التخزين ذات الحجم الحرفي. ال حجم() يحتوي عامل التشغيل على مُعامل واحد يمكن أن يكون إما تعبيرًا أو طباعة بيانات حيث يكون الإرسال هو نوع بيانات محاط بين قوسين. لا يمكن أن يكون نوع البيانات مجرد أنواع بيانات بدائية مثل أنواع البيانات الصحيحة أو العائمة، ولكن يمكن أيضًا أن يكون أنواع بيانات المؤشر وأنواع البيانات المركبة مثل الاتحادات والبنيات.
الحاجة إلى مشغل sizeof()
بشكل أساسي، تعرف البرامج حجم تخزين أنواع البيانات البدائية. على الرغم من أن حجم تخزين نوع البيانات ثابت، إلا أنه يختلف عند تنفيذه في منصات مختلفة. على سبيل المثال، نقوم بتخصيص مساحة المصفوفة ديناميكيًا باستخدام حجم() المشغل أو العامل:
int *ptr=malloc(10*sizeof(int));
في المثال أعلاه، نستخدم عامل التشغيل sizeof()، والذي يتم تطبيقه على قالب من النوع int. نحن نستخدم مالوك () وظيفة لتخصيص الذاكرة وإرجاع المؤشر الذي يشير إلى هذه الذاكرة المخصصة. مساحة الذاكرة تساوي عدد البايتات التي يشغلها نوع البيانات int ومضروبة في 10.
ملحوظة:
يمكن أن يختلف الإخراج على أجهزة مختلفة، مثل نظام التشغيل 32 بت سيُظهر مخرجات مختلفة، وسيُظهر نظام التشغيل 64 بت مخرجات مختلفة لنفس أنواع البيانات.
ال حجم() يتصرف المشغل بشكل مختلف وفقًا لنوع المعامل.
عندما يكون المعامل هو نوع البيانات.
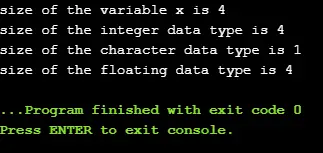
#include int main() { int x=89; // variable declaration. printf('size of the variable x is %d', sizeof(x)); // Displaying the size of ?x? variable. printf('
size of the integer data type is %d',sizeof(int)); //Displaying the size of integer data type. printf('
size of the character data type is %d',sizeof(char)); //Displaying the size of character data type. printf('
size of the floating data type is %d',sizeof(float)); //Displaying the size of floating data type. return 0; } في الكود أعلاه، نقوم بطباعة حجم أنواع البيانات المختلفة مثل int وchar وfloat بمساعدة حجم() المشغل أو العامل.
انتاج |
عندما يكون المعامل تعبيرا
#include int main() { double i=78.0; //variable initialization. float j=6.78; //variable initialization. printf('size of (i+j) expression is : %d',sizeof(i+j)); //Displaying the size of the expression (i+j). return 0; } في الكود أعلاه، قمنا بإنشاء متغيرين 'i' و 'j' من النوع double و float على التوالي، ثم نقوم بطباعة حجم التعبير باستخدام حجم (ط + ي) المشغل أو العامل.
انتاج |
size of (i+j) expression is : 8
التعامل مع المصفوفات والهياكل
ال حجم المشغل (). يعد مفيدًا للغاية عند العمل مع المصفوفات والهياكل بالإضافة إلى حالات الاستخدام المذكورة أعلاه. كتل متجاورة من الذاكرة المعروفة باسم صفائف ، وفهم حجمها أمر بالغ الأهمية لعدد قليل من المهام.
شجرة بتري وشجرة ب
على سبيل المثال:
#include int main() { int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; int arrSize = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); printf('Size of the array arr is: %d
', sizeof(arr)); printf('Number of elements in arr is: %d
', arrSize); return 0; } انتاج |
Size of the array arr is: 20 Number of elements in arr is: 5
إرجاع Sizeof(arr). الحجم الإجمالي للمصفوفة بالبايت، بينما حجم(ar[0]) تقوم بإرجاع أصغر حجم للعنصر في المصفوفة. يتم تحديد عدد العناصر في المصفوفة عن طريق قسمة الحجم الإجمالي على حجم المصفوفة عنصر واحد (arrSize) . باستخدام هذه التقنية، سوف يستمر الكود مرن في مواجهة أحجام المصفوفة المتغيرة.
جافا سكريبت للقائمة المنسدلة
وبالمثل، يمكنك استخدام حجم المشغل (). لمعرفة حجم الهياكل:
#include struct Person { char name[30]; int age; float salary; }; int main() { struct Person p; printf('Size of the structure Person is: %d bytes
', sizeof(p)); return 0; } انتاج |
Size of the structure Person is: 40 bytes
تخصيص الذاكرة الديناميكية وحساب المؤشر
تطبيقات أخرى لل حجم المشغل (). يشمل حساب المؤشر و تخصيص الذاكرة الديناميكية . تصبح معرفة حجم أنواع البيانات أمرًا ضروريًا عند العمل معها صفائف و مؤشرات لتخصيص الذاكرة الصحيح والوصول إلى العناصر.
#include #include int main() { int *ptr; int numElements = 5; ptr = (int*)malloc(numElements * sizeof(int)); if (ptr == NULL) { printf('Memory allocation failed!
'); return 1; } for (int i = 0; i <numelements; i++) { ptr[i]="i" + 1; } printf('dynamic array elements: '); for (int i="0;" < numelements; printf('%d ', ptr[i]); free(ptr); release allocated memory. return 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Dynamic array elements: 1 2 3 4 5 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In this example, a size <strong> <em>numElements integer</em> </strong> array has a memory that is dynamically allocated. <strong> <em>numElements * sizeof(int)</em> </strong> bytes represent the total amount of memory allocated. By doing this, the array is guaranteed to have enough room to accommodate the desired amount of integers.</p> <h2>Sizeof() for Unions</h2> <p> <strong> <em>Unions</em> </strong> and the <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> are compatible. <strong> <em>Unions</em> </strong> are comparable to <strong> <em>structures,</em> </strong> except only one member can be active at once, and all its members share memory.</p> <pre> #include union Data { int i; float f; char str[20]; }; int main() { union Data data; printf('Size of the union Data is: %d bytes
', sizeof(data)); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Size of the union Data is: 20 bytes </pre> <p>The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is extremely important since it's essential for <strong> <em>memory management</em> </strong> , <strong> <em>portability</em> </strong> , and <strong> <em>effective data handling</em> </strong> . The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is crucial in C for the reasons listed in the list below:</p> <p> <strong>Memory Allocation:</strong> When working with <strong> <em>arrays</em> </strong> and <strong> <em>dynamic memory allocation</em> </strong> , the <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is frequently used in memory allocation. Knowing the size of <strong> <em>data types</em> </strong> when allocating memory for arrays or structures guarantees that the correct amount of memory is reserved, reducing <strong> <em>memory overflows</em> </strong> and improving memory utilization.</p> <p> <strong>Portability:</strong> Since C is a <strong> <em>popular programming language</em> </strong> , code frequently has to operate on several systems with differing architectures and <strong> <em>data type sizes</em> </strong> . As it specifies the size of data types at compile-time, the <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> aids in designing portable code by enabling programs to adapt automatically to various platforms.</p> <p> <strong>Pointer Arithmetic:</strong> When dealing with pointers, the <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> aids in figuring out <strong> <em>memory offsets</em> </strong> , allowing accurate movement within <strong> <em>data structures, arrays</em> </strong> , and other memory regions. It is extremely helpful when iterating across arrays or dynamically allocated memory.</p> <p> <strong>Handling Binary Data:</strong> The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> guarantees that the right amount of data is read or written when working with binary data or files, eliminating mistakes brought on by inaccurate data size assumptions.</p> <p> <strong>Unions and Structures:</strong> The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is essential when managing <strong> <em>structures</em> </strong> and <strong> <em>unions</em> </strong> , especially when utilizing them to build complicated data structures. <strong> <em>Memory allocation</em> </strong> and access become effective and error-free when you are aware of the size of structures and unions.</p> <p> <strong>Safe Buffer Management:</strong> The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> helps make sure that the buffer is big enough to hold the data being processed while working with character <strong> <em>arrays (strings)</em> </strong> , preventing <strong> <em>buffer overflows</em> </strong> and <strong> <em>potential security flaws</em> </strong> .</p> <p> <strong>Data Serialization and Deserialization:</strong> The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> guarantees that the right amount of data is handled, maintaining <strong> <em>data integrity</em> </strong> throughout <strong> <em>data transfer</em> </strong> or storage, in situations where data needs to be serialized (converted to a byte stream) or deserialized (retrieved from a byte stream).</p> <p> <strong>Code Improvement:</strong> Knowing the size of various data formats might occasionally aid in <strong> <em>code optimization</em> </strong> . For instance, it enables the compiler to more effectively align data structures, reducing memory waste and enhancing cache performance.</p> <h2>Sizeof() Operator Requirement in C</h2> <p>The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is a key component in C programming due to its need in different elements of memory management and data processing. Understanding <strong> <em>data type</em> </strong> sizes is essential for <strong> <em>effectively allocating memory</em> </strong> , especially when working with arrays and dynamic memory allocation. By ensuring that the appropriate amount of memory is reserved, this information helps to avoid memory overflows and optimize memory use. The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is also essential for creating <strong> <em>portable code</em> </strong> , which may execute without <strong> <em>error</em> </strong> on several systems with differing architectures and data type sizes.</p> <p>The program can adapt to many platforms without the need for manual modifications since it supplies the size of data types at compile-time. Additionally, the <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> makes it possible to navigate precisely around data structures and arrays while working with pointers, facilitating safe and effective pointer arithmetic. Another application for the <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is handling <strong> <em>unions</em> </strong> and <strong> <em>structures</em> </strong> . It ensures precise memory allocation and access within intricate <strong> <em>data structures</em> </strong> , preventing mistakes and inefficiencies. The <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is a basic tool that enables C programmers to develop effective, portable, and resilient code while optimizing performance and data integrity. It ensures <strong> <em>safe buffer management</em> </strong> and makes data serialization and deserialization easier.</p> <h2>Conclusion:</h2> <p>In summary, the <strong> <em>C sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is a useful tool for calculating the size of many sorts of objects, including <strong> <em>data types, expressions, arrays, structures, unions</em> </strong> , and more. As it offers the size of data types at compile-time, catering to multiple platforms and settings, it enables programmers to create portable and flexible code. Developers may effectively handle <strong> <em>memory allocation, pointer arithmetic</em></strong> , and <strong> <em>dynamic memory allocation</em> </strong> in their programs by being aware of the storage needs of various data types.</p> <p>When working with <strong> <em>arrays</em> </strong> and <strong> <em>structures</em> </strong> , the <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> is very helpful since it ensures proper <strong> <em>memory allocation</em> </strong> and makes it simple to retrieve elements. Additionally, it facilitates <strong> <em>pointer arithmetic</em> </strong> , making it simpler to move between memory regions. However, because of operator precedence, programmers should be cautious when utilizing complicated expressions with <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> .</p> <p>Overall, learning the <strong> <em>sizeof() operator</em> </strong> equips C programmers to create stable and adaptable software solutions by enabling them to write efficient, dependable, and platform-independent code.</p> <hr></numelements;> توضيح:
في هذا المثال، حجم عدد صحيح من العناصر يحتوي المصفوفة على ذاكرة يتم تخصيصها ديناميكيًا. عدد العناصر * حجم (كثافة العمليات) تمثل البايتات إجمالي مقدار الذاكرة المخصصة. من خلال القيام بذلك، يتم ضمان وجود مساحة كافية للمصفوفة لاستيعاب الكمية المطلوبة من الأعداد الصحيحة.
Sizeof() للنقابات
النقابات و ال حجم المشغل (). متوافقة. النقابات قابلة للمقارنة ل الهياكل، باستثناء عضو واحد فقط يمكن أن يكون نشطًا في الوقت نفسه، ويتشارك جميع أعضائه في الذاكرة.
#include union Data { int i; float f; char str[20]; }; int main() { union Data data; printf('Size of the union Data is: %d bytes
', sizeof(data)); return 0; } انتاج |
Size of the union Data is: 20 bytes
ال حجم المشغل (). مهم للغاية لأنه ضروري ل إدارة الذاكرة , قابلية التنقل ، و التعامل الفعال مع البيانات . ال حجم المشغل (). يعد أمرًا بالغ الأهمية في لغة C للأسباب المذكورة في القائمة أدناه:
تخصيص الذاكرة: عند العمل مع صفائف و تخصيص الذاكرة الديناميكية ، ال حجم المشغل (). كثيرا ما يستخدم في تخصيص الذاكرة. معرفة حجم أنواع البيانات عند تخصيص الذاكرة للصفائف أو الهياكل يضمن حجز المقدار الصحيح من الذاكرة، مما يقلل تفيض الذاكرة وتحسين استخدام الذاكرة.
قابلية التنقل: بما أن C هو أ لغة البرمجة الشعبية ، يجب أن يعمل الكود في كثير من الأحيان على عدة أنظمة ذات بنيات وأنظمة مختلفة أحجام نوع البيانات . نظرًا لأنه يحدد حجم أنواع البيانات في وقت الترجمة، فإن حجم المشغل (). يساعد في تصميم التعليمات البرمجية المحمولة من خلال تمكين البرامج من التكيف تلقائيًا مع الأنظمة الأساسية المختلفة.
حساب المؤشر: عند التعامل مع المؤشرات، حجم المشغل (). يساعد في معرفة تعويضات الذاكرة ، مما يسمح بحركة دقيقة داخل هياكل البيانات، المصفوفات ومناطق الذاكرة الأخرى. إنه مفيد للغاية عند التكرار عبر المصفوفات أو الذاكرة المخصصة ديناميكيًا.
ما هو الفرق بين الميجابايت والجيجابايت
التعامل مع البيانات الثنائية: ال حجم المشغل (). يضمن قراءة أو كتابة الكمية المناسبة من البيانات عند العمل مع البيانات أو الملفات الثنائية، مما يزيل الأخطاء الناجمة عن افتراضات حجم البيانات غير الدقيقة.
النقابات والهياكل: ال حجم المشغل (). أمر ضروري عند الإدارة الهياكل و النقابات خاصة عند استخدامها لبناء هياكل بيانات معقدة. تخصيص الذاكرة ويصبح الوصول فعالاً وخاليًا من الأخطاء عندما تكون على دراية بحجم الهياكل والنقابات.
إدارة المخزن المؤقت الآمن: ال حجم المشغل (). يساعد على التأكد من أن المخزن المؤقت كبير بما يكفي لاستيعاب البيانات التي تتم معالجتها أثناء العمل مع الأحرف المصفوفات (سلاسل) ، منع تجاوزات المخزن المؤقت و العيوب الأمنية المحتملة .
تسلسل البيانات وإلغاء التسلسل: ال حجم المشغل (). يضمن التعامل مع الكمية المناسبة من البيانات والحفاظ عليها تكامل البيانات طَوَال نقل البيانات أو التخزين، في الحالات التي تحتاج فيها البيانات إلى إجراء تسلسل (تحويل إلى دفق بايت) أو إلغاء تسلسلها (استرجاعها من دفق بايت).
تحسين الكود: قد تساعد معرفة حجم تنسيقات البيانات المختلفة في بعض الأحيان تحسين الكود . على سبيل المثال، فهو يمكّن المترجم من محاذاة هياكل البيانات بشكل أكثر فعالية، مما يقلل من هدر الذاكرة ويعزز أداء ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت.
متطلبات المشغل Sizeof() في C
ال حجم المشغل (). يعد مكونًا رئيسيًا في برمجة C نظرًا لحاجته إلى عناصر مختلفة لإدارة الذاكرة ومعالجة البيانات. فهم نوع البيانات الأحجام ضرورية ل تخصيص الذاكرة بشكل فعال خاصة عند العمل مع المصفوفات وتخصيص الذاكرة الديناميكية. من خلال التأكد من حجز المقدار المناسب من الذاكرة، تساعد هذه المعلومات على تجنب تجاوز سعة الذاكرة وتحسين استخدام الذاكرة. ال حجم المشغل (). ضروري أيضًا للإنشاء الكود المحمول ، والتي قد يتم تنفيذها بدون خطأ على العديد من الأنظمة ذات البنى المختلفة وأحجام أنواع البيانات.
يمكن للبرنامج التكيف مع العديد من الأنظمة الأساسية دون الحاجة إلى تعديلات يدوية لأنه يوفر حجم أنواع البيانات في وقت الترجمة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، حجم المشغل (). يجعل من الممكن التنقل بدقة حول هياكل البيانات والمصفوفات أثناء العمل باستخدام المؤشرات، مما يسهل عملية حسابية آمنة وفعالة للمؤشر. تطبيق آخر ل حجم المشغل (). يتم التعامل النقابات و الهياكل . فهو يضمن تخصيصًا دقيقًا للذاكرة والوصول إليها ضمن نطاق معقد هياكل البيانات ، ومنع الأخطاء وأوجه القصور. ال حجم المشغل (). هي أداة أساسية تمكن مبرمجي لغة C من تطوير تعليمات برمجية فعالة ومحمولة ومرنة مع تحسين الأداء وسلامة البيانات. إنه يضمن إدارة المخزن المؤقت الآمن ويجعل تسلسل البيانات وإلغاء التسلسل أسهل.
خاتمة:
باختصار، C sizeof () عامل التشغيل هي أداة مفيدة لحساب حجم العديد من أنواع الكائنات، بما في ذلك أنواع البيانات، التعبيرات، المصفوفات، الهياكل، الاتحادات ، و اكثر. نظرًا لأنه يوفر حجم أنواع البيانات في وقت الترجمة، ويلبي منصات وإعدادات متعددة، فإنه يمكّن المبرمجين من إنشاء تعليمات برمجية محمولة ومرنة. يمكن للمطورين التعامل بفعالية تخصيص الذاكرة، المؤشر الحسابي ، و تخصيص الذاكرة الديناميكية في برامجهم من خلال إدراك احتياجات التخزين لأنواع البيانات المختلفة.
عند العمل مع صفائف و الهياكل ، ال حجم المشغل (). مفيد جدًا لأنه يضمن السليم تخصيص الذاكرة ويجعل من السهل استرداد العناصر. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإنه يسهل حساب المؤشر مما يسهل التنقل بين مناطق الذاكرة. ومع ذلك، بسبب أسبقية المشغل، يجب على المبرمجين توخي الحذر عند استخدام التعبيرات المعقدة مع حجم المشغل (). .
على العموم تعلم حجم المشغل (). يزود مبرمجي C بإنشاء حلول برمجية مستقرة وقابلة للتكيف من خلال تمكينهم من كتابة تعليمات برمجية فعالة وموثوقة ومستقلة عن النظام الأساسي.
