نظرا أ شجرة ثنائية خاصة لمن العقد الورقية ترتبط بتشكيل أ قائمة دائرية مرتبطة بشكل مضاعف المهمة هي العثور على ارتفاع من الشجرة.
أمثلة:
مدخل:
جافا مقارنة السلاسل
الإخراج: 2
توضيح: ارتفاع الشجرة الثنائية بعد التعرف على العقد الورقية هو 2. في الشجرة الثنائية أعلاه، 6 5 و 4 عبارة عن عقد ورقية وتشكل قائمة دائرية مرتبطة بشكل مزدوج. هنا سيكون المؤشر الأيسر للعقدة الطرفية بمثابة المؤشر السابق للقائمة الدائرية المرتبطة بشكل مضاعف وسيكون المؤشر الأيمن بمثابة المؤشر التالي للقائمة الدائرية المرتبطة بشكل مضاعف.مدخل:
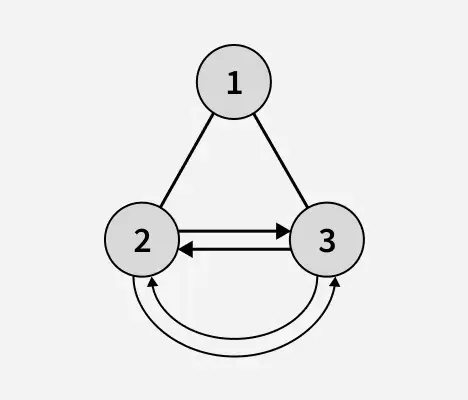
الإخراج: 1
توضيح: ارتفاع الشجرة الثنائية بعد التعرف على العقد الورقية هو 1. في الشجرة الثنائية أعلاه، 2 و 3 عبارة عن عقد ورقية وتشكل قائمة دائرية مرتبطة بشكل مزدوج.تحويل سلسلة إلى عدد صحيح
يقترب :
C++الفكرة هي المتابعة نهج مماثل كما نفعل ل العثور على ارتفاع شجرة ثنائية عادية . نحن بشكل متكرر احسب ارتفاع ل اليسار واليمين الأشجار الفرعية للعقدة وتعيينها ارتفاع إلى العقدة كما الأعلى من ارتفاعات طفلين زائد 1. لكن الطفل الأيسر والأيمن لـ أ عقدة الورقة تكون فارغة بالنسبة للأشجار الثنائية العادية. لكن العقدة الورقية هنا هي عقدة قائمة دائرية مرتبطة بشكل مزدوج. لذا، لكي تكون العقدة عقدة ورقية، فإننا نتحقق مما إذا كانت العقدة اليسرى واليمنى ويشير إلى العقدة ولها اليمين واليسار ويشير أيضا إلى العقدة نفسها.
// C++ program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// C program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// Java program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static boolean isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; System.out.println(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
# Python program to calculate height of a special tree # whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # function to check if given # node is a leaf node or node def isLeaf(node): # For a node to be a leaf node it should # satisfy the following two conditions: # 1. Node's left's right pointer should be # current node. # 2. Node's right's left pointer should be # current node. # If one condition is met it is guaranteed # that the other condition is also true. return (node.left and node.left.right == node and node.right and node.right.left == node) # Compute the height of a tree def findTreeHeight(node): # if node is NULL return -1. if node is None: return -1 # if node is a leaf node return 0 if isLeaf(node): return 0 # compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)) if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.left.left.left = Node(6) # Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes l1 = root.left.left.left l2 = root.left.right l3 = root.right # create circular doubly linked list out of # leaf nodes of the tree # set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2 l2.right = l3 l3.right = l1 # set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2 l2.left = l1 l1.left = l3 print(findTreeHeight(root))
// C# program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static bool isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.Max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } static void Main(string[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; Console.WriteLine(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
// JavaScript program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node function isLeaf(node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left && node.left.right === node && node.right && node.right.left === node; } // Compute the height of a tree function findTreeHeight(node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node === null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes const l1 = root.left.left.left; const l2 = root.left.right; const l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; console.log(findTreeHeight(root));
الإخراج
3
تعقيد الوقت: يا(ن) أين ن هو عدد العقد.
المساحة المساعدة: أوه)


